Incorporating reclaimed wood usage inside residential and commercial building initiatives provides a classy resolution for designers and homeowners looking for sustainability with out compromising aesthetic attraction or marcenaria Em osasco structural integrity. Reclaimed wood—salvaged from old buildings, barns, warehouses, and even discarded furniture—provides a singular blend of history, texture, and sturdiness that's unattainable with newly sourced timber. Beyond creating beautiful visible impression, reclaimed wood addresses trendy concerns similar to environmental preservation, cost-efficiency, and enhanced property value, making it a robust materials alternative aligned with modern constructing standards and home-owner priorities.
Understanding Reclaimed Wood: Origins, Characteristics, and Classification
To leverage reclaimed wood effectively, it is important to comprehend its origins and inherent qualities. This detailed understanding ensures informed selections relating to its selection, treatment, and utility inside building or renovation projects.
Sources and Types of Reclaimed Wood
Reclaimed wooden originates from a wide selection of sources: deconstructed older houses, barns, factories, delivery pallets, and river logs recovered from post-industrial environments. Materials harvested from these sources range significantly in species, age, and condition, influencing their suitability for specific functions. For occasion, wood from early 20th-century barns generally exhibits tighter growth rings indicating slow growth and resulting in denser, higher-quality lumber. Common varieties embody oak, pine, chestnut, and fir—all prized for their unique grain patterns and sturdiness.
Correctly figuring out the wood species and its history helps anticipate its conduct beneath stress, susceptibility to pests, and response to fashionable finishes and adhesives, important components to maintaining compliance with contemporary building codes.
Material Properties: Strength, Stability, and Aesthetics
One of the best benefits of reclaimed wood lies in its enhanced mechanical power and stability. Many older timbers had been harvested from mature bushes grown in dense forests, producing wooden with tighter development rings and fewer defects in comparison with fashionable, fast-grown lumber. This intrinsic density lends superior load-bearing capabilities and dimensional stability, usually exceeding those of comparable new wood.
Aesthetically, reclaimed wood brings warm patinas, irregular grain patterns, nail holes, and knots that create a textured, history-rich ambiance. This weathered character is extremely sought after for designing interiors that reflect authenticity and craftsmanship. Beyond beauty, these textures offer practical benefits—increased surface roughness improves adhesion when applying finishes or structural parts, enhancing long-term efficiency.
Classification Systems and Grading of Reclaimed Wood
Reclaimed wood should undergo grading and classification aligned with requirements corresponding to those from the American Lumber Standard Committee (ALSC) or the National Wood Flooring Association (NWFA), depending on software. This grading accounts for elements like structural integrity, presence of defects, and contaminants. Structural reclaimed wood usually achieves grades corresponding to Grade No. 1 or No. 2 timber utilized in framing. Flooring and cladding-grade woods focus more on aesthetics and floor put on resistance.
Understanding these classification nuances ensures compliance with both safety rules and design intent, permitting builders and inspectors to approve reclaimed wood with out unnecessary delays or costly rework.
The Environmental and Economic Benefits of Reclaimed Wood in Construction
With growing awareness of ecological impact and rising material prices, reclaimed wooden usage delivers compelling environmental and monetary benefits beyond its aesthetic enchantment.
Carbon Footprint Reduction and Resource Conservation
Harvesting virgin timber contributes considerably to deforestation and marcenaria em osasco carbon emissions. Utilizing reclaimed wooden mitigates these issues by extending the lifecycle of current materials, lowering the demand for new logging operations. This follow aligns with LEED certification requirements and other sustainability frameworks promoting eco-friendly constructing supplies.
Moreover, reclaiming wood conserves landfill area by diverting sizable amounts of timber waste generated from demolition tasks. This waste discount has ancillary benefits corresponding to lower transportation emissions and decreased want for synthetic landfill covers or methane management systems.
Cost Effectiveness and Long-Term Value
While reclaimed wood can initially seem expensive because of labor-intensive salvage and processing methods, it usually results in important financial savings over the lifecycle of a project. Reclaimed wood’s superior durability reduces maintenance and alternative costs. Additionally, its unique appearance could allow owners and developers to command larger resale values or rental premiums—key drivers in competitive actual estate markets.
When integrated thoughtfully, reclaimed wooden enhances property marketability and might contribute positively to appraisal values as a outcome of its association with high quality craftsmanship and sustainable residing.
Compatibility with Modern Construction and Design Trends
Modern architecture more and more highlights the mixing of pure materials with industrial or minimalist design sensibilities. Reclaimed wooden matches completely within features like exposed beams, accent walls, or customized cabinetry, balancing chilly steel or concrete surfaces with warmth and texture. This compatibility allows versatile functions, making it a well-liked material for architects and interior designers aiming for timeless but contemporary areas.
Technical Considerations for Reclaimed Wood in Building Projects
Effective use of reclaimed wood requires deep perception into treatment, preparation, and regulatory compliance. This part dissects technical challenges and options making certain safety, longevity, and performance.
Inspection and Hazard Identification
Salvaged wood may carry hidden dangers such as embedded nails, insect injury, fungal decay, or chemical contamination (e.g., lead-based paints or creosote preservatives). Prior to any use, reclaimed wooden must endure rigorous inspection including visual analysis, moisture content measurement, and generally non-destructive testing strategies.
Identifying structural defects early prevents failures that compromise building security and incur costly repairs. Implementing standardized inspection protocols supports certification for reuse and adheres to native constructing codes and occupational safety guidelines.
Cleaning, Processing, and Restoration Methods
Post-inspection, reformas Residenciais the wooden requires thorough cleaning to take away filth, mold, and preservatives incompatible with trendy finishes. Mechanical cleaning strategies (e.g., sanding, planing) are commonplace, however must be fastidiously applied to avoid extreme thinning. Chemical treatments may also be employed to neutralize pest infestations or contaminants, but selection is important to avoid introducing new toxicants.
Restoration often entails milling to attain uniform dimensions and regrading to certify strength and suitability. Automated slicing instruments paired with guide ending protect the character of the wooden whereas enabling accurate set up.
Structural Integration and Code Compliance
When incorporating reclaimed wooden into structural components such as beams, posts, or flooring systems, it's essential to confirm that it meets local building codes and engineering standards. Factors like load-bearing capability, fireplace resistance ratings, and fastening methods must align with regulatory requirements.
Engineers could require stress testing or certification by licensed structural professionals before approving reclaimed lumber for crucial functions. Additionally, applicable design allowances ought to be made for differential shrinkage and motion over time.
Applications of Reclaimed Wood Across Home Renovations and Commercial Projects
From delicate accents to main structural elements, reclaimed wood’s versatility caters to a broad vary of design and functional wants.
Interior Features: Flooring, Walls, Ceilings, and Furnishings
One of the most popular uses of reclaimed wooden is in flooring, the place durability and patina are aesthetically paramount. Properly milled reclaimed boards, when put in with moisture control strategies, excel in high-traffic residential and business areas. Similarly, reclaimed wooden paneling adds warmth and character to walls and ceilings, creating inviting areas that mix rustic charm with trendy design.
Custom furnishings and cabinetry crafted from reclaimed wood elevate interiors by incorporating historical texture paired with up to date performance. These pieces usually function focal elements that resonate with homeowners’ need for meaningful, individualized spaces.
Structural Elements: Beams, Columns, and Framework
Structural reuse of reclaimed timber calls for scrutiny however presents substantial benefits when executed appropriately. Large, dense beams reclaimed from older constructions typically surpass new equivalents in strength and stability. When built-in, they contribute to sustainable development goals and enhance indoor environmental high quality by reducing VOC emissions from new treated lumber.
Furthermore, reformas Pequenas visible publicity of those components creates dramatic architectural statements, enhancing perceived house worth and attracting discerning patrons or tenants.
Exterior Uses: Siding, Decking, and Landscaping
Reclaimed wood used in exterior functions must endure weathering, UV exposure, and moisture cycles. With correct treatment—including sealing, staining, and applying UV inhibitors—it performs properly as siding or decking material, offering a historic aesthetic that new supplies cannot replicate.
Landscaping components, corresponding to pergolas, planter boxes, and fencing, also profit from reclaimed wood, providing value savings and eco-conscious attraction. However, exterior installations require vigilant upkeep plans to extend life and preserve security.
Design Strategies and Psychological Impacts of Reclaimed Wood in Living Spaces
Material choice speaks volumes about occupant values and way of life preferences. Reclaimed wood carries psychological and design implications that transcend mere functionality.
Emotional Connection and Sense of History
Incorporating reclaimed wood fosters a tangible link to the previous, inviting occupants to expertise a narrative embedded inside each knot and grain variation. This emotional resonance typically creates emotions of heat, security, and identity, elevating the overall residing expertise.
In business spaces, this emotional storytelling can encourage longer dwell instances, consumer loyalty, and enhanced brand perception. For owners, it transforms rooms into living artwork, adding intangible worth to on a daily basis environments.
Balancing Rustic Charm with Modern Aesthetic Principles
Expert design balances reclaimed wood’s raw, rustic options with clear modern lines, ensuring spaces really feel recent and intentional somewhat than outdated. Mixing reclaimed elements with modern metals, glass, or neutral color palettes results in dynamic contrasts that enchantment to a large demographic, from traditionalists to modernists.
This stability also facilitates advertising properties to broader audiences and encourages design longevity, reducing the necessity for frequent remodels driven by shifting stylistic tendencies.
Impact on Indoor Air Quality and Health
Using reclaimed wood as an alternative of composite or chemically treated materials can significantly cut back exposure to volatile organic compounds (VOCs), bettering indoor air quality. Well-processed reclaimed wooden supports more healthy environments by minimizing artificial chemical off-gassing and fostering natural humidity regulation due to its hygroscopic properties.
This issue is increasingly essential for families with allergies, asthma, or chemical sensitivities, contributing to improved long-term health and luxury.
Summary and Practical Next Steps for Integrating Reclaimed Wood
Reclaimed wood usage stands at the intersection of sustainability, design innovation, and sensible development. Its distinctive blend of robustness, environmental responsibility, and timeless aesthetics provides multifaceted advantages that handle contemporary challenges in building and renovation.
Key insights include:
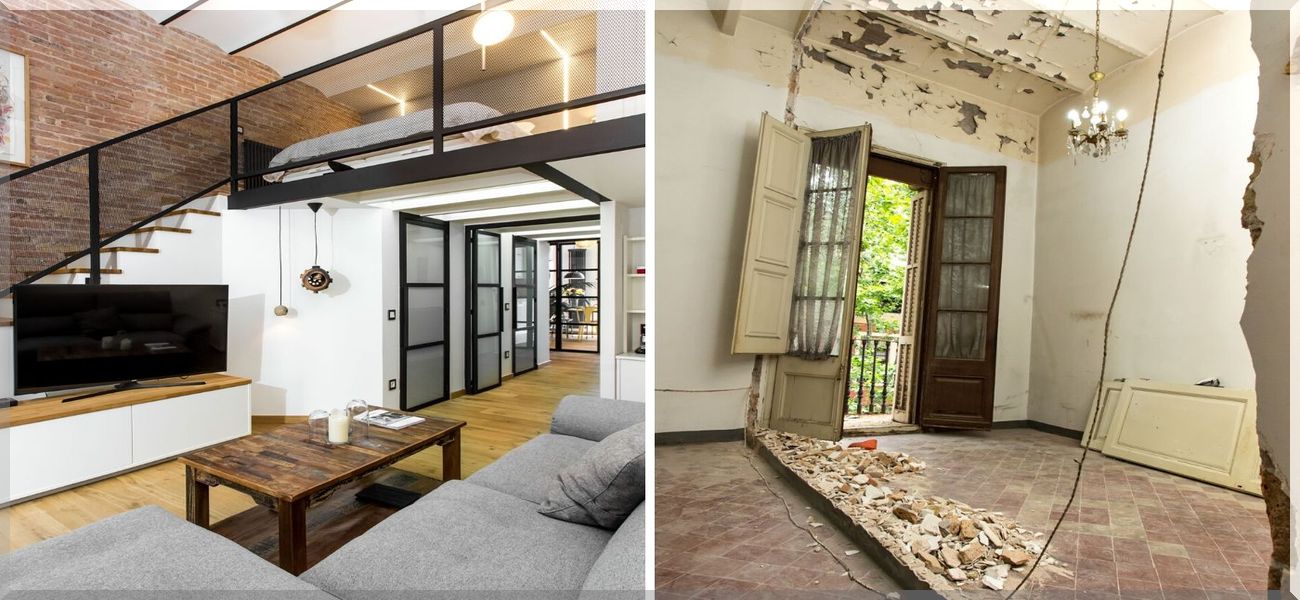

- Reclaimed wood’s superior durability and distinctive appearance elevate property values while supporting eco-conscious building objectives.
- Careful inspection, processing, marcenaria em osasco and adherence to building codes are important to making sure safety, compliance, and long-term performance.
- Versatile functions vary from ornamental interiors to crucial structural parts, each requiring tailored treatment and design strategies.
- The psychological and well being advantages underscore reclaimed wood’s contribution to improved living quality and occupant well-being.
For professionals and householders able to combine reclaimed wooden:
- Begin by sourcing reputable suppliers specializing in certified reclaimed timber to ensure quality and traceability.
- Conduct thorough web site assessments to find out one of the best application types suited to your project’s design and functional objectives.
- Collaborate with structural engineers and licensed inspectors early to validate reuse methods and doc compliance.
- Incorporate design components that highlight reclaimed wood’s natural history while guaranteeing complementary modern finishes and fixtures.
- Plan for acceptable upkeep regimes, particularly for exterior installations, to maximise longevity and aesthetic attraction.
Adopting reclaimed wooden thoughtfully paves the way for buildings that are not only beautiful and durable but also function enduring testaments to resourceful, accountable, and inspired design.